weic2428 — Science Release
Webb finds surprises in Spiderweb protocluster field
4 December 2024
Using the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope, an international team of astronomers have found new galaxies in the Spiderweb protocluster. Their characteristics shed light on the growth of galaxies in these large cosmic cities, with the finding that gravitational interactions in these dense regions are not as important as previously thought.
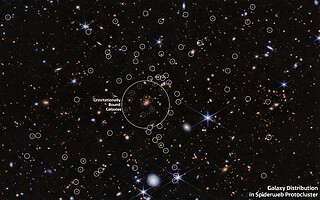
Astronomers explore galaxy populations and uncover their physical characteristics across large-scale structures to better understand the build-up of galaxies and how their environments shape their assembly. The Spiderweb protocluster is a well-studied object in the early Universe. Its light has travelled over 10 billion years to reach us, and it shows us a galaxy cluster in formation, composed of more than a hundred known galaxies.
With the use of Webb’s capabilities, astronomers have now sought to better understand this protocluster and to reveal new galaxies inside it. Infrared light passes more freely through cosmic dust than visible light, which is scattered by the dust. Because Webb can see infrared light very well, scientists used it to observe regions of the Spiderweb that were previously hidden to us by cosmic dust, and to find out to what degree this dust obscures them.
“We are observing the build-up of one the largest structures in the Universe, a city of galaxies in construction,” explained Jose M. Pérez-Martínez of the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias and the Universidad de La Laguna in Spain. “We know that most galaxies in local galaxy clusters (the biggest metropolises of the Universe) are old and not very active, whereas in this work we are looking at these objects during their adolescence. As this city in construction grows, their physical properties will also be affected. Now, Webb is giving us new insights into the build-up of such structures for the first time.”
Webb enabled the team to study the hydrogen gas using a powerful diagnostic tracer that cannot be studied from ground-based observations. That allowed the team to reveal new, strongly obscured galaxies belonging to the cluster and to study how much they were obscured. This was accomplished using only about 3.5 hours of Webb’s observing time.
“As expected, we found new galaxy cluster members, but we were surprised to find more than expected,” explained Rhythm Shimakawa of Waseda University in Japan. “We found that previously-known galaxy members (similar to the typical star-forming galaxies like our Milky Way galaxy) are not as obscured or dust-filled as previously expected, which also came as a surprise.”
“This can be explained by the fact that the growth of these typical galaxies is not triggered primarily by galaxy interactions or mergers that induce star-formation,” added Helmut Dannerbauer of the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias in Spain. “We now figure this can instead be explained by star formation that is fueled through gas accumulating at different locations all across the object’s large-scale structure.”
The new results used Webb’s NIRCam observations (Cycle 1 programme #1572, PIs: H. Dannerbauer and Y. Koyama) and are featured in two papers that have been published today in the Astrophysical Journal. The team is planning to study the (new) galaxy cluster members in more detail and confirm their existence with spectroscopic observations using Webb.
More information
Webb is the largest, most powerful telescope ever launched into space. Under an international collaboration agreement, ESA provided the telescope’s launch service, using the Ariane 5 launch vehicle. Working with partners, ESA was responsible for the development and qualification of Ariane 5 adaptations for the Webb mission and for the procurement of the launch service by Arianespace. ESA also provided the workhorse spectrograph NIRSpec and 50% of the mid-infrared instrument MIRI, which was designed and built by a consortium of nationally funded European Institutes (The MIRI European Consortium) in partnership with JPL and the University of Arizona.
Webb is an international partnership between NASA, ESA and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
Image Credit: ESA/Webb, NASA & CSA, H. Dannerbauer
Links
- Science paper (R. Shimakawa et. al)
- Science paper (J. M. Pérez-Martínez et. al)
- Release on ESA website
Contacts
Helmut Dannerbauer
Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, Spain
Email: [email protected]
Bethany Downer
ESA/Webb Chief Science Communications Officer
Email: [email protected]
Ninja Menning
ESA Newsroom and Media Relations Office
Email: [email protected]
About the Release
| Release No.: | weic2428 | |
|---|---|---|