weic2302 — Science Release
Webb Confirms Its First Exoplanet
11 January 2023
Researchers have confirmed the presence of an exoplanet, a planet that orbits another star, using the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope for the first time. Formally classified as LHS 475 b, the planet is almost exactly the same size as our own, clocking in at 99% of Earth’s diameter.
The research team is led by Kevin Stevenson and Jacob Lustig-Yaeger, both of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland. The team chose to observe this target with Webb after carefully reviewing data from NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) which hinted at the planet’s existence. Webb’s Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) captured the planet easily and clearly with only two transit observations. “There is no question that the planet is there. Webb’s pristine data validate it,” said Lustig-Yaeger. “The fact that it is also a small, rocky planet is impressive for the observatory,” Stevenson added.
“These first observational results from an Earth-sized, rocky planet open the door to many future possibilities for studying rocky planet atmospheres with Webb,” agreed Mark Clampin, Astrophysics Division director at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “Webb is bringing us closer and closer to a new understanding of Earth-like worlds outside the Solar System, and the mission is only just getting started.”
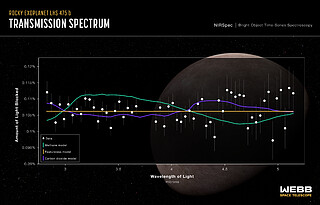
Among all operating telescopes, only Webb is capable of characterising the atmospheres of Earth-sized exoplanets. The team attempted to assess what is in the planet’s atmosphere by analysing its transmission spectrum. Although the data show that this is an Earth-sized terrestrial planet, they do not yet know if it has an atmosphere. “The observatory’s data are beautiful,” said Erin May, also of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory. “The telescope is so sensitive that it can easily detect a range of molecules, but we can’t yet draw any definitive conclusions about the planet’s atmosphere.”
Although the team can’t conclude what is present, they can definitely say what is not present. “There are some terrestrial-type atmospheres that we can rule out,” explained Lustig-Yaeger. “It can’t have a thick methane-dominated atmosphere, similar to that of Saturn’s moon Titan.”
The team also notes that while it’s possible the planet has no atmosphere, there are some atmospheric compositions that have not been ruled out, such as a pure carbon dioxide atmosphere. “Counterintuitively, a 100% carbon dioxide atmosphere is so much more compact that it becomes very challenging to detect,” said Lustig-Yaeger. Even more precise measurements are required for the team to distinguish a pure carbon dioxide atmosphere from no atmosphere at all. The researchers are scheduled to obtain additional spectra with further observations this summer.
Webb also revealed that the planet is a few hundred degrees warmer than Earth, so if clouds are detected it may lead the researchers to conclude that the planet is more like Venus, which has a carbon dioxide atmosphere and is perpetually shrouded in thick cloud. “We’re at the forefront of studying small, rocky exoplanets,” Lustig-Yaeger said. “We have barely begun scratching the surface of what their atmospheres might be like.”
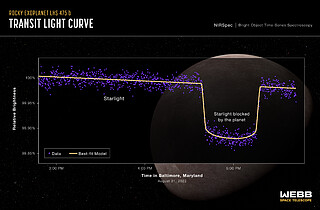
The researchers also confirmed that the planet completes an orbit in just two days, information that was almost instantaneously revealed by Webb’s precise light curve. Although LHS 475 b is closer to its star than any planet in the Solar System, its red dwarf star is less than half the temperature of the Sun, so the researchers project it still could support an atmosphere.
The researchers’ findings have opened up the possibility of pinpointing Earth-sized planets orbiting smaller red dwarf stars. “This rocky planet confirmation highlights the precision of the mission’s instruments,” Stevenson said. “And it is only the first of many discoveries that it will make.” Lustig-Yaeger agreed: “With this telescope, rocky exoplanets are the new frontier.”
LHS 475 b is relatively close, at only 41 light-years away, in the constellation Octans.
The team’s results were presented at a press conference of the American Astronomical Society (AAS) on Wednesday 11 January, 2023.
More information
Webb is the largest, most powerful telescope ever launched into space. Under an international collaboration agreement, ESA provided the telescope’s launch service, using the Ariane 5 launch vehicle. Working with partners, ESA was responsible for the development and qualification of Ariane 5 adaptations for the Webb mission and for the procurement of the launch service by Arianespace. ESA also provided the workhorse spectrograph NIRSpec and 50% of the mid-infrared instrument MIRI, which was designed and built by a consortium of nationally funded European Institutes (The MIRI European Consortium) in partnership with JPL and the University of Arizona.
Webb is an international partnership between NASA, ESA and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, L. Hustak (STScI)
Links
- Collection of Webb’s First Images
- ESA Webb Seeing Farther Interactive Brochure
- Spectroscopy with Webb
- Release on STScI website
- Release on ESA website
- Release on NASA website
Contacts
Bethany Downer
ESA/Webb Chief Science Communications Officer
Email: [email protected]
Ninja Menning
ESA Newsroom and Media Relations Office
Email: [email protected]
About the Release
| Release No.: | weic2302 | |
|---|---|---|